↔️ Elastic Scaling
On the Scale page, you can configure the two scaling options: horizontal and vertical. Horizontal scaling refers to the number of instances (replicas), while vertical scaling involves the CPU and memory requests and limits.
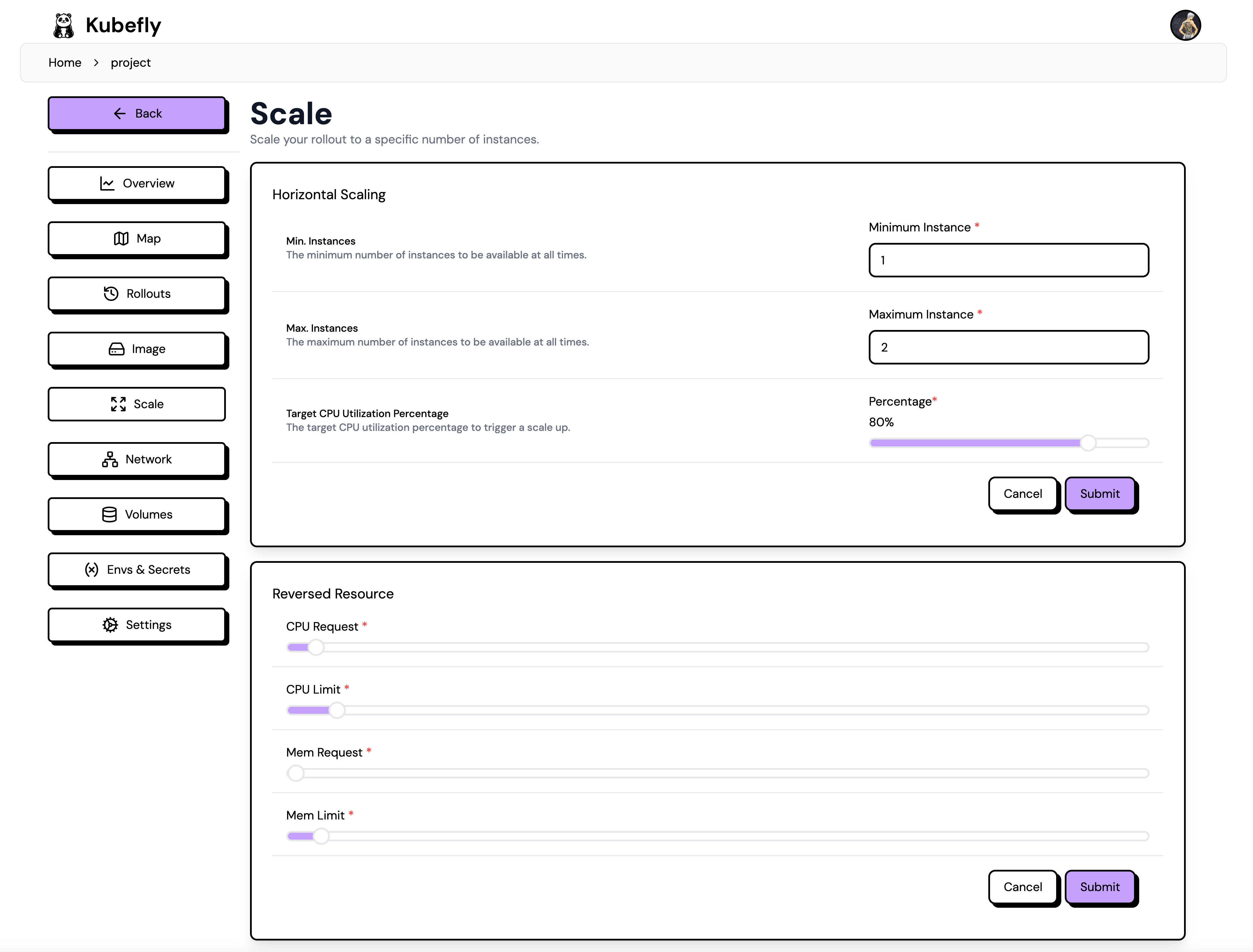
Horizontal
You can define the minimum and maximum number of replicas. The target CPU defines the autoscaling behavior. If the CPU usage exceeds the target CPU, the replicas will be scaled up. To view the current CPU usage, you can visit the deployment overview page.
Vertical
Vertical scaling refers to the CPU and memory requests and limits. The request is the minimum amount of CPU and memory that the pod will receive. The limit is the maximum amount of CPU and memory that the pod can use. If the pod exceeds this limit, it will be terminated. Requests and limits are defined in millicores and megabytes (MB). The limit should be equal to or higher than the request.
Make sure you understand your application's requirements to set the appropriate values. If you are unsure of the requirements, you can start with the default values and monitor the behavior. If you notice that the pod is being terminated due to exceeding the limit, you can increase the limit.